ACI 347.3R-14, “Guide for the Safety of Formwork, Shoring, and Scaffolding”, is a comprehensive document published by the American Concrete Institute (ACI) that provides guidelines to ensure safety in the use of formwork, shoring, and scaffolding in construction projects. It primarily focuses on the safety practices and design considerations required for these temporary structures, which are essential for supporting concrete during construction until it has cured and gained sufficient strength.
Here’s a summary of the key aspects covered in the guide:
1. General Safety Considerations
- Hazards Identification: Emphasizes the identification of hazards associated with formwork, shoring, and scaffolding. This includes the risk of collapse, falls, and material handling issues.
- Personnel Training: Requires proper training for workers handling or working around these systems to reduce the risk of accidents.
- Inspection Requirements: Inspections should be conducted before and during the construction process, focusing on the condition of materials, connections, and the overall integrity of the systems.
2. Formwork Safety
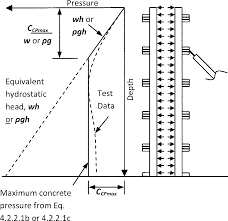
- Design Criteria: The guide outlines the importance of designing formwork to withstand both the weight of the fresh concrete and any live loads that might occur during construction. It also stresses the need to account for environmental factors such as wind and seismic loads.
- Support Systems: Includes recommendations for ensuring that formwork support systems are stable and properly braced to avoid collapse.
3. Shoring Safety
- Shoring Equipment: Shoring is used to support formwork and other loads until the concrete structure can support itself. ACI 347.3R discusses the proper use, inspection, and maintenance of shoring equipment, which may include posts, beams, and jacks.
- Load Calculations: Shoring systems should be designed to handle the loads imposed by both fresh concrete and any additional live loads, like workers or equipment.
- Load Distribution: Guidelines for ensuring that the load from formwork is evenly distributed through the shoring system to avoid local overloading.
4. Scaffolding Safety
- Types of Scaffolding: The guide covers the different types of scaffolding systems used in construction, including frame scaffolds, tube-and-clamp systems, and suspended scaffolds. Each has unique safety considerations.
- Stability and Guardrails: Specific focus on ensuring scaffolding is stable and that guardrails, toe boards, and other protective elements are in place to prevent falls.
- Loading Limits: Scaffolding should be designed and maintained to support the loads placed on it, including workers, tools, and materials.
5. Construction and Erection Practices
- Erection and Dismantling: Provides safety protocols for the erection and dismantling of formwork, shoring, and scaffolding, focusing on sequence and stability. Safe practices should be followed to minimize risks during these operations.
- Material Handling: Emphasizes safe procedures for handling materials, including lifting, moving, and securing formwork components.
6. Monitoring and Adjustments
- Monitoring During Construction: Ongoing monitoring of formwork, shoring, and scaffolding is critical to detect early signs of failure. Adjustments may be required as construction progresses, particularly if unexpected loads or environmental conditions arise.
- Safety Measures during Concrete Pouring: Special attention is given to the safety measures needed during the pouring process, particularly regarding the behavior of the formwork as it is subjected to the weight of fresh concrete.
7. Workforce and Management Responsibilities
- Supervision and Coordination: The importance of adequate supervision and coordination among workers, engineers, and safety personnel to ensure safe practices are maintained throughout the construction process.
- Safety Plans: The guide recommends developing a detailed safety plan specific to each project that accounts for the risks associated with formwork, shoring, and scaffolding.
8. Regulatory Compliance
- Standards and Regulations: ACI 347.3R advises adherence to local, state, and federal regulations, including OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) standards and other relevant safety codes.
9. References and Additional Resources
- The guide also provides references to related documents and standards, such as ACI 347 (Formwork for Concrete) and various OSHA guidelines.
This document serves as a resource to ensure that the design, installation, and removal of formwork, shoring, and scaffolding is done in a manner that prioritizes the safety of workers and the stability of the structure. It provides not just design considerations, but practical safety procedures and guidelines for managing the temporary structures throughout the construction process.