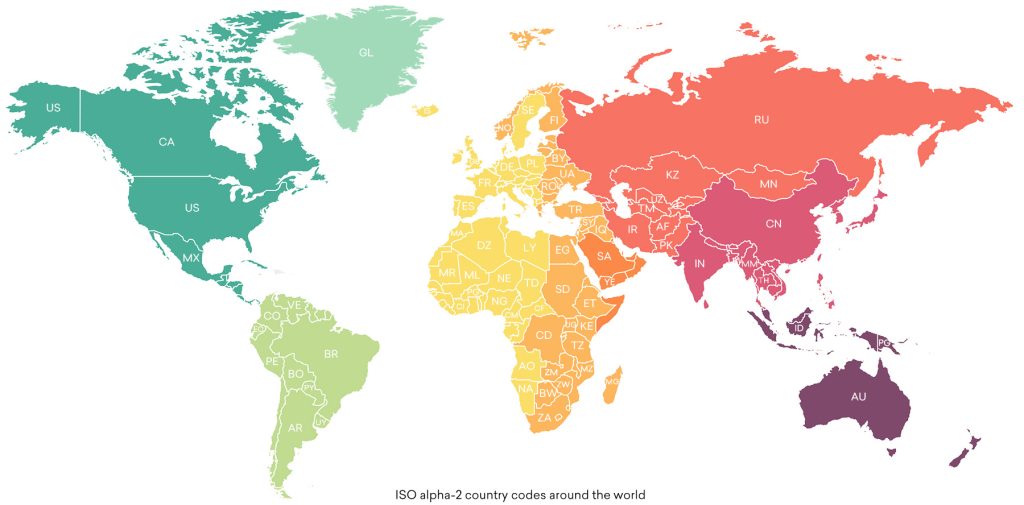
ISO Country Codes are standardized codes assigned to countries and territories, developed and maintained by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). These codes are used globally for consistency in identifying countries in data systems, documents, and communications. They are defined in the ISO 3166 standard, which includes three parts:
ISO 3166-1: Codes for countries
This part provides codes for currently existing countries and territories. It includes:
- Alpha-2 code: Two-letter code used commonly in country abbreviations (e.g., US for the United States, IN for India).
- Widely used in international contexts, such as top-level domain names (e.g.,
.us,.uk).
- Widely used in international contexts, such as top-level domain names (e.g.,
- Alpha-3 code: Three-letter code providing a closer association with the country’s name (e.g., USA for the United States, IND for India).
- Often used in databases and international trade systems.
- Numeric code: Three-digit numeric code (e.g., 840 for the United States, 356 for India).
- Useful for systems where non-Latin scripts are used.
ISO 3166-2: Codes for subdivisions
This part assigns codes for subdivisions within countries, such as states, provinces, or regions.
- Format: [Alpha-2 country code]-[Subdivision code] (e.g., US-CA for California in the United States, IN-MH for Maharashtra in India).
ISO 3166-3: Codes for formerly used country names
This part assigns codes for countries or territories that have changed names or ceased to exist.
- Example: CSXX was assigned to Serbia and Montenegro after it split into Serbia (RS) and Montenegro (ME).
Applications of ISO Country Codes
Finance: Used in banking and monetary systems (e.g., SWIFT codes).
Trade and logistics: Used in customs declarations and international shipping.
Internet domains: Used for country-code top-level domains (ccTLDs).
Data exchange: Facilitates interoperability across databases and software.
Sports: Used by international organizations (e.g., FIFA, Olympics) to represent countries.