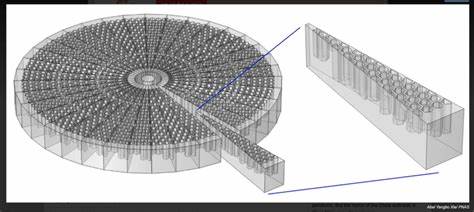
Here’s an overview of earthquake-resistant construction techniques using advanced materials:
1. Base Isolation Systems
Description: Base isolation involves placing bearings or pads between a building’s foundation and superstructure.
Advanced Materials:
- Lead-Rubber Bearings (LRB) – Combines rubber layers with lead core, allowing flexibility and energy dissipation.
- High-Damping Rubber Bearings (HDRB) – Rubber with additives to enhance energy absorption.
- Friction Pendulum Bearings – Use sliding surfaces with special materials like stainless steel and PTFE (Teflon).
Benefit: Reduces seismic forces transferred to the structure.
2. Seismic Dampers
Description: Dissipate seismic energy to reduce motion.
Advanced Materials:
- Viscoelastic Dampers – Use polymers that deform and absorb energy during earthquakes.
- Fluid Viscous Dampers (FVD) – Use silicone-based fluids to convert kinetic energy to heat.
- Magnetorheological Dampers (MR) – Fluids with magnetic particles change viscosity under electromagnetic fields.
Benefit: Increases damping capacity and prevents structural damage.
3. Shape Memory Alloys (SMA)
Description: Alloys that return to their original shape after deformation.
Material: Nickel-Titanium (Nitinol) alloys.
Application: Used in reinforcement bars, braces, and connectors.
Benefit: High elasticity, self-centering ability, and excellent fatigue resistance.
4. Fiber-Reinforced Polymers (FRP)
Description: Lightweight, high-strength composites for retrofitting and strengthening.
Materials: Carbon fiber, glass fiber, aramid fiber.
Application: Wrapped around columns, beams, and joints to enhance tensile strength.
Benefit: Corrosion-resistant, high durability, and easy to apply to existing structures.
5. Ultra-High-Performance Concrete (UHPC)
Description: A dense, high-strength concrete with superior durability and crack resistance.
Materials: Steel fibers, silica fume, and nano-silica.
Application: Bridge piers, shear walls, and building cores.
Benefit: Withstands extreme forces and minimizes structural damage.
6. Self-Healing Concrete
Description: Concrete that repairs its own cracks through embedded capsules or bacteria.
Materials: Microcapsules filled with epoxy or limestone-producing bacteria.
Application: Foundations, walls, and bridges.
Benefit: Enhances longevity and reduces maintenance.
7. Geopolymer Concrete
Description: Environmentally friendly concrete made from industrial by-products.
Materials: Fly ash, slag, and alkali activators.
Application: Infrastructure, retrofitting.
Benefit: High early strength, reduced carbon footprint, and excellent fire resistance.
8. Flexible Building Materials
Description: Materials that allow controlled deformation under seismic loads.
Materials: Engineered timber (CLT – Cross Laminated Timber), bamboo, and ductile metals.
Application: Modular buildings, low-rise structures.
Benefit: Lightweight, sustainable, and flexible.
9. 3D Printing in Seismic Design
Description: Additive manufacturing of custom structural components.
Materials: High-strength concrete, composite polymers.
Application: Customized joints, structural reinforcements.
Benefit: Rapid, cost-effective, and adaptable designs. evolving challenge, but through research, innovative materials, and thoughtful planning, we can build structures that not only survive extreme weather but also provide long-term sustainability for communities.