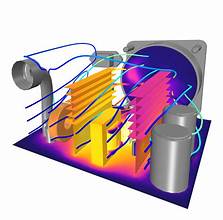
COMSOL Multiphysics is a powerful and versatile software platform designed for simulating a wide range of physical phenomena through numerical methods. It provides a comprehensive environment for modeling coupled, or “multiphysics,” systems, where multiple physical processes interact and affect one another. One of its key strengths is its ability to handle complex simulations that span across different engineering disciplines, including fluid dynamics, structural mechanics, heat transfer, electromagnetics, and chemical reactions.
The software’s CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) capabilities are a core feature, allowing users to model fluid flow, heat transfer, and related phenomena. With COMSOL’s CFD module, users can simulate laminar and turbulent flow, convection, heat conduction, and more, in both steady-state and transient scenarios. It offers a variety of solvers and meshing techniques to accommodate the needs of different applications, whether for simple laminar flows or highly complex turbulent systems.
Key features of COMSOL’s multiphysics and CFD capabilities include:
- Multiphysics Coupling: COMSOL excels in the integration of different physical models. For instance, fluid flow can be coupled with heat transfer, structural mechanics, electromagnetics, or chemical reactions, providing a holistic view of the system’s behavior.
- Customizable Interfaces: COMSOL offers specialized interfaces for specific applications like heat transfer, fluid flow, or acoustics. These interfaces come with predefined settings and tools to streamline the simulation setup process.
- Meshing Tools: The software includes powerful meshing capabilities to create accurate computational grids, including unstructured meshes for complex geometries. It also supports automatic mesh refinement in areas of high-gradient behavior, ensuring precise results.
- Solver Flexibility: COMSOL offers several solver options, including direct and iterative solvers, adaptive solvers, and domain-specific solvers, which are optimized for different physical phenomena and system sizes.
- Post-Processing and Visualization: COMSOL’s visualization tools provide users with detailed graphical representations of simulation results, such as flow patterns, temperature distributions, stress fields, and more. It supports 2D and 3D plots, animations, and interactive result exploration.
- Multiphysics Simulation Workflow: The software’s environment is built for a streamlined workflow, allowing users to define geometry, physics, mesh, solvers, and post-processing steps in a unified interface. Users can also create custom simulations using COMSOL’s built-in programming language, MATLAB, or by adding external functionality through the COMSOL Application Builder.
- High-Performance Computing: COMSOL supports parallel computing and high-performance clusters, making it suitable for large-scale simulations requiring significant computational power.
COMSOL’s CFD and multiphysics capabilities are widely used in various industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, energy, and chemical engineering for applications ranging from product design and optimization to troubleshooting and research. The software’s flexibility and depth make it a preferred tool for engineers and researchers tackling complex, real-world problems.