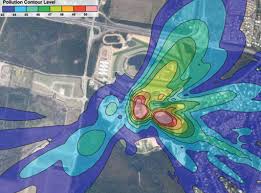
CALPUFF is a widely used air quality modeling system developed by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) for evaluating the transport, transformation, and deposition of air pollutants in complex terrain. It is designed to simulate the dispersion of pollutants over long distances and takes into account factors like topography, meteorological conditions, and chemical reactions.
Key Features of CALPUFF:
- Multiscale Modeling: CALPUFF is a flexible system that can model pollutants across a range of spatial scales—from small local areas to larger regional scales.
- Complex Terrain: One of its core strengths is the ability to handle complex topography and meteorological conditions, which is critical for areas with uneven terrain like mountains or valleys.
- Multiple Pollutants: It can simulate the dispersion of a wide variety of pollutants, including both gaseous and particulate matter.
- Meteorological Input: CALPUFF requires detailed meteorological data (such as wind speed, temperature, and humidity) for accurate simulations, typically provided by the user or generated from meteorological models.
- Chemical Transformations: The model incorporates the ability to simulate pollutant transformations, such as chemical reactions that occur in the atmosphere, which is essential for simulating pollutants like sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and nitrogen oxides (NOₓ).
- Wet and Dry Deposition: It can estimate pollutant deposition onto surfaces, both through dry deposition and by precipitation (wet deposition), which is important for assessing the impact of pollutants on ecosystems.
- Use Cases: CALPUFF is used in regulatory contexts for environmental assessments, especially for National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) compliance, as well as in permit applications for sources like power plants, industrial facilities, and transportation corridors.
CALPUFF Components:
- CALMET: A meteorological preprocessor used to generate gridded meteorological fields that are input to the CALPUFF model.
- CALPOST: A postprocessor that helps in analyzing and visualizing the results from CALPUFF.
- CALPUFF: The core dispersion model that simulates the transport and transformation of pollutants.
Applications:
- Regulatory Modeling: CALPUFF is used in regulatory settings for air quality management and to assess the impact of new sources on ambient air quality.
- Environmental Impact Assessments (EIA): It helps evaluate how projects (e.g., new industrial facilities, highways) will affect local and regional air quality.
- Public Health Studies: The model is used in studies related to public health impacts due to air pollution exposure.
- Climate Studies: It is sometimes used to analyze atmospheric processes like the dispersion of greenhouse gases.
Strengths and Limitations:
Limitations: The accuracy of the model depends heavily on the quality of input data, including meteorological data and emission inventories. Additionally, CALPUFF may require significant computational resources for large-scale simulations.
Strengths: CALPUFF is particularly useful for cases involving complex terrain and long-range pollutant transport. Its ability to handle different types of pollutants and meteorological conditions makes it highly versatile.