The term “Gaussian” refers to anything related to the mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss and his work on the normal distribution, which is commonly referred to as a Gaussian distribution. It is a bell-shaped curve that is symmetric about the mean, with its values tapering off as you move away from the center. This distribution is fundamental in statistics and appears in various fields, including physics, economics, and machine learning.
Some key aspects of the Gaussian function include:
- Gaussian Distribution: It describes how values are distributed in a population. The probability density function (PDF) for a Gaussian distribution is given by:f(x)=1σ2πe−(x−μ)22σ2f(x) = \frac{1}{\sigma \sqrt{2 \pi}} e^{-\frac{(x – \mu)^2}{2 \sigma^2}}f(x)=σ2π1e−2σ2(x−μ)2Where:
- μ\muμ is the mean (center of the distribution),
- σ\sigmaσ is the standard deviation (which controls the spread),
- xxx is the variable.
- Gaussian Function: In mathematics, the Gaussian function is typically represented as f(x)=e−x2f(x) = e^{-x^2}f(x)=e−x2, which describes a smooth curve centered at zero and decaying rapidly as you move away from the origin. This function is important in many areas of analysis and signal processing.
- Applications: The Gaussian distribution is widely used because of its central role in the Central Limit Theorem, which states that the sum of a large number of independent random variables tends toward a Gaussian distribution, regardless of the original distribution. It also appears in signal processing, where Gaussian filters are used to blur or smooth data.
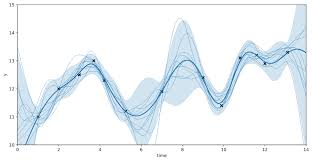
- Gaussian Process: In machine learning, a Gaussian process is a collection of random variables, any finite number of which have a joint Gaussian distribution. It is a powerful tool for regression, classification, and optimization, especially when the data is noisy or when you need to make predictions based on limited data.
- Gaussian Blur: In image processing, Gaussian blur is a technique used to smooth or blur images. It works by averaging the pixels in a neighborhood around each pixel, weighted by a Gaussian distribution. This helps reduce noise and detail in the image.
Gaussian methods are pervasive because they often represent idealized conditions or assumptions in statistical modeling, making them valuable across many fields.