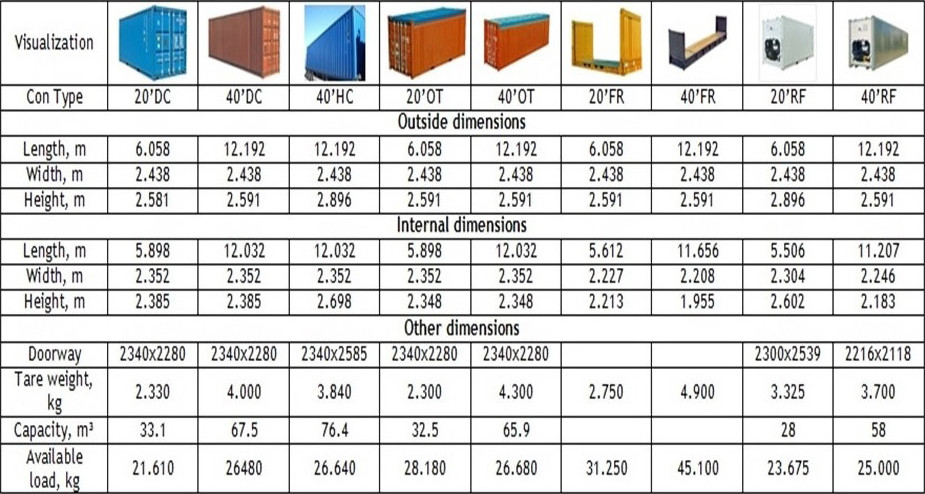
ISO codes for measurements refer to standardized abbreviations and representations of units of measurement, defined by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). These codes are part of ISO 80000, which outlines quantities and units used across various disciplines, and other related standards. Here’s an overview of ISO codes for measurements:
ISO 80000
ISO 80000 provides a standard for quantities and units, divided into multiple parts:
- ISO 80000-1 to ISO 80000-13:
- Covers various areas like space and time, mechanics, thermodynamics, electromagnetism, acoustics, and more.
- Defines units like meters (m), kilograms (kg), seconds (s), kelvins (K), and coulombs (C).
- Common Units and Their Codes:
- Length: meter (m), kilometer (km), centimeter (cm)
- Mass: gram (g), kilogram (kg), tonne (t)
- Time: second (s), minute (min), hour (h)
- Electric Current: ampere (A)
- Temperature: kelvin (K), degree Celsius (°C)
- Amount of Substance: mole (mol)
- Luminous Intensity: candela (cd)
- Prefixes for SI Units:
- Commonly used prefixes are included for scaling units.
- milli- (m), centi- (c), kilo- (k), mega- (M), giga- (G), etc.
- Example: kilometer (km), millisecond (ms), gigabyte (GB).
- Commonly used prefixes are included for scaling units.
ISO 31 (Obsolete, Replaced by ISO 80000)
ISO 31 was the predecessor to ISO 80000 and laid the foundation for standardized measurement codes.
Other Related ISO Standards
- ISO 2955:
- Specifies codes for units of measurement, particularly for use in computer systems.
- Examples:
mfor meterkgfor kilogramAfor amperesfor second
- ISO 8601:
- Related to date and time representations.
- Used for coding durations (e.g., “P1Y2M10D” for 1 year, 2 months, 10 days).
Why Use ISO Codes for Measurements?
Clarity: Avoids ambiguities in abbreviations and notations. APIs, databases, and international communication due to their unambiguous nature and global standardization.
Uniformity: Enables consistent communication across international systems.
Interoperability: Essential for data exchange in engineering, science, and commerce.