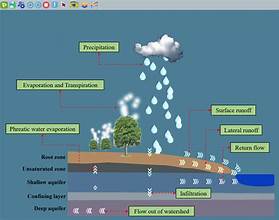
The Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) is a robust, comprehensive hydrological model developed for simulating the impacts of land management practices on water, sediment, and agricultural chemical yields in large, complex watersheds. It is widely used for watershed modeling and management, offering valuable insights into water quality and quantity under various conditions and scenarios.
Key Features and Components:
- Hydrological Modeling: SWAT simulates the water cycle, including surface runoff, percolation, evapotranspiration, and groundwater flow. This helps in understanding streamflow, soil erosion, and water availability.
- Land Management Simulation: The model integrates various land use types, soil properties, topography, and management practices. It assesses how practices like crop rotation, tillage, and fertilization influence water resources and soil health.
- Sediment and Nutrient Transport: SWAT can model the movement of sediments and nutrients (such as nitrogen and phosphorus) through watersheds, helping to evaluate non-point source pollution and water quality impacts.
- Weather Data Integration: The model relies on climatic inputs such as precipitation, temperature, wind, and solar radiation to simulate hydrological processes and provide predictions across different weather conditions.
- Watershed Calibration and Validation: SWAT uses historical data (streamflow, sediment, and water quality data) to calibrate and validate model parameters, ensuring that the simulation results closely reflect real-world observations.
- Scenario Analysis: The tool allows users to evaluate different land use or management strategies and predict their impacts on watershed health. This is vital for decision-making regarding conservation practices and policy development.
- Long-term Forecasting: SWAT supports long-term predictions, allowing users to assess the effects of climate change, urbanization, or changing agricultural practices over time.
Applications:
- Water Quality Management: SWAT helps identify pollution sources and evaluates the effectiveness of control measures, such as best management practices (BMPs).
- Flood Prediction and Management: The tool can simulate flood events by predicting runoff in response to varying rainfall events.
- Conservation Planning: It is used to determine the most effective conservation practices for reducing soil erosion and nutrient loss.
- Climate Change Impact Studies: SWAT models can assess how changing weather patterns might influence water resources, agricultural productivity, and ecosystem health.
Advantages:
- Scalability: SWAT is capable of simulating both small watersheds and large river basins, making it adaptable to a wide range of applications.
- Data Integration: It integrates various datasets such as land use, soil properties, and climate data, which helps in producing more accurate results.
- User-friendly Interface: With tools like ArcSWAT (an ArcGIS extension), users can easily interact with spatial data and visualize model outputs.
Limitations:
- Data Requirement: High-quality and spatially distributed data are essential for accurate model predictions, which can be difficult to obtain in certain regions.
- Complexity: The model can be challenging for beginners to use effectively without a strong understanding of hydrology and GIS (Geographic Information Systems).
In conclusion, SWAT is a powerful tool for watershed modeling and management. It helps decision-makers understand the effects of land management practices on hydrological and environmental processes, supporting sustainable water resources management and effective land use planning.